1. Understand the Blanking Line Workflow
A typical blanking line involves several integrated processes, including uncoiling, leveling, Laser Cutting, and blanking. Each stage contributes to the quality of the final part:
Uncoiling: Proper handling of metal coils prevents scratches, dents, or deformation. Ensuring the coil is correctly aligned is critical for downstream processes.
Leveling: Flattening the sheet removes residual stresses and ensures uniform thickness, which is crucial for precise blanking and smooth laser cutting.
Laser Cutting: Incorporating laser cutting in the blanking line improves accuracy, produces smooth edges, and allows complex geometries with minimal burrs.
Blanking: This stage shears the sheet into the desired shapes and sizes. Tooling condition and line speed directly affect part quality.
Understanding the complete workflow allows operators to optimize each stage, from uncoiling to laser cutting, ensuring consistent high-quality results.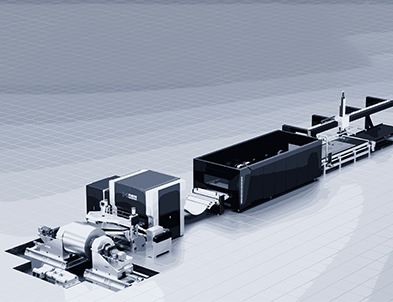
2. Use High-Quality Material
The quality of the Sheet Metal itself has a direct impact on blanked parts. Tips include:
Consistent Thickness: Variations can affect leveling and laser cutting precision.
Surface Finish: Avoid sheets with scratches or rust, as these can interfere with clean cuts and tool life.
Material Suitability: High-strength or coated steels may require adjustments to laser cutting settings and blanking pressure.
High-quality materials reduce rework, extend tool life, and improve outcomes in uncoiling, leveling, and laser cutting stages.
3. Maintain Precision Tooling
Tooling is critical for producing high-quality parts:
Inspection: Regularly check punches, dies, and laser optics for wear or damage.
Alignment: Ensure proper alignment of the die and laser system for clean cuts and precise blanks.
Edge Sharpness: Sharp tooling and correctly tuned laser cutting parameters minimize burrs and deformation.
Lubrication: Reduces friction in leveling rollers and die contacts, enhancing part quality.
4. Optimize Line Speed and Pressure
Line speed and press force affect part quality:
Feed Speed: Too fast can cause sheet misalignment during uncoiling and uneven blanks; too slow reduces productivity.
Press Force: Adequate pressure ensures complete blanking without overloading tooling.
Laser Parameters: Adjust laser cutting speed and power based on material type and thickness for clean cuts.
Proper optimization across uncoiling, leveling, and laser cutting ensures clean, precise blanks.
5. Implement Regular Quality Checks
Consistent quality requires monitoring:
Dimensional Accuracy: Check blanks after leveling and laser cutting.
Edge Quality: Inspect for burrs, cracks, or incomplete cuts.
Surface Flatness: Leveling ensures flat sheets for accurate blanking.
Sampling: Regular checks during production detect issues early.
6. Reduce Scrap and Waste
Efficient material use is critical:
Nesting Software: Optimizes laser cutting patterns for maximum yield.
Tool Clearance: Correct punch and die spacing reduces scrap and edge imperfections.
Recycling: Collect and recycle scrap metal wherever possible.
7. Maintain Proper Machine Alignment
Roller and Guides: Proper alignment during leveling prevents uneven sheets.
Punch and Laser Alignment: Misalignment affects blank quality.
Sensor Calibration: Ensures accuracy in uncoiling, leveling, and laser cutting.
8. Consider Automation and Monitoring
Automation enhances precision:
Automated Feeding: Reduces manual handling during uncoiling.
Laser Monitoring: Real-time laser cutting inspection ensures consistent results.
Predictive Maintenance: Alerts operators to worn rollers, dies, or laser components.
9. Operator Training
Skilled operators optimize uncoiling, leveling, and laser cutting processes:
Equipment Knowledge: Understand machine functions and controls.
Problem-Solving: Quickly detect misfeeds, burrs, or deformation.
Material Expertise: Adjust laser cutting settings and blanking pressure for different metals.
10. Maintain a Clean Production Environment
Dust and Debris: Remove particles that affect leveling rollers and laser cutting optics.
Lighting: Ensures defects are detected early.
Safety Protocols: Protect equipment and personnel during high-speed blanking operations.
Conclusion
Producing high-quality sheet metal parts requires attention to each stage of the blanking line, especially uncoiling, leveling, and laser cutting. By maintaining precise tooling, optimizing line speed, performing regular inspections, and training operators, manufacturers can ensure precise, consistent, and high-quality blanks.
A well-managed blanking line improves efficiency, reduces waste, and supports sustainable manufacturing, while modern techniques like laser cutting enhance precision and flexibility in sheet metal production.









